Definition: The Universal or Ideal Gas Law describes the relationship between all four properties (pressure, volume, number of moles, and temperature) as well as a gas constant called “R.”
NOTE: The Ideal Gas Constant “R” has constant a value of 0.0821 L.atm/mol.K
Relation: The relation between pressure (P) volume (V), number of moles (n) and temperature (T) remain the same as in other gas laws:
- Pressure (P) is indirectly proportional to volume (V).
- Volume (V) is directly proportional to temperature (T) and number of moles (n).
- Temperature (T) is directly proportional to Pressure (P).
Equation: PV = nRT
NOTE: This gas law must use the same units as those found in the Ideal Gas Constant, R. Otherwise the units will not cancel out when the equation is solved.
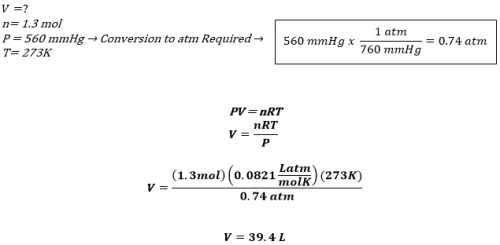
Problem: What is the volume of 1.3 mol of HCl gas at 560mmHg pressure and 273K?
GIVEN: