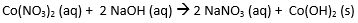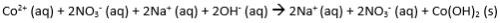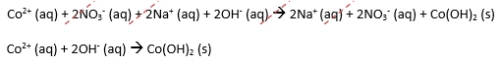Typically you will be asked to further dissect a chemical equation by writing not only the molecular equation, but additionally the complete ionic and net ionic equations.
- The molecular equation is the full balance chemical equation.
- The complete ionic equation is the entire chemical equation with all aqueous substances dissociated into their respective ions. NOTE: gases, solids, and liquids DO NOT dissociate and remain in their molecular forms!
- The net ionic equation is what is left at the end of the reaction, after the spectator ions have been eliminated.
NOTE: spectator ions are ions that appear on both sides of the chemical equation that are eliminated before the net ionic equation is written. Like spectators at a sporting event, they are not directly involved and are therefore not part of the main attraction.
Example:
Molecular Equation:
Complete Ionic Equation:
Net Ionic Equation:
Notice how the net ionic equation gives you the essence of the reaction: a precipitate was formed with Co and OH reacted. It’s the bottom line of the reaction.